In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, where online transactions have become the norm, payment processing lies at the heart of seamless and secure commerce. However, behind the scenes, a dynamic duel takes place: the battle between front-end and back-end payment processing. Like two sides of a coin, these two components play distinct yet interconnected roles, driving the gears of our financial transactions.
In this captivating exploration, we delve into the realm of front-end and back-end payment processing, unraveling their mysteries and shedding light on the vital role they play in shaping our digital economy. Join us on this exhilarating journey as we unveil the intricacies of these formidable forces that make e-commerce possible.
How Payment Processing Works?
Payment processing is a complex system that enables the seamless transfer of funds between buyers and sellers in the digital world. The process begins when a customer initiates a payment by providing their payment information. This data is securely transmitted through payment gateways to the acquiring bank or payment processor.
The payment information undergoes a validation process, including checks for sufficient funds and fraud prevention. The payment processor then sends an authorization request to the issuing bank for approval. If approved, the payment processor notifies the merchant of the successful transaction. The customer’s account is debited, and the funds are held by the acquiring bank.
The settlement process follows, where the payment processor collaborates with the acquiring bank to transfer the funds from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account. This involves clearinghouses and payment networks to facilitate secure fund transfers. Once the settlement is complete, the transaction is considered finalized, and the merchant can access the funds. This intricate orchestration of data transmission, authentication, and settlement ensures the integrity and security of digital transactions, empowering businesses and consumers in the modern economy.
What is Front-End Processing?
Front-end processing, also known as front-end payment processing, refers to the initial stage of a payment transaction where the customer’s payment information is collected and validated. It involves the interface and systems interacting directly with the customer during the payment process.

When a customer initiates a payment, whether it’s through a website, mobile app, or point-of-sale terminal, the front-end processing comes into play. It typically involves the following steps:
Payment Information Collection
The customer provides their payment details, such as credit card information, billing address, and any additional verification data required.
Data Encryption and Security
The collected payment data is encrypted using secure protocols to ensure its confidentiality and protection from unauthorized access.
Validation and Verification
The front-end system validates the payment data, performing checks to ensure the information provided is complete, accurate, and meets the required format and security standards. This includes verifying the card number, expiration date, CVV code and performing address verification.
User Experience and Interface
The front-end processing focuses on providing a user-friendly and intuitive interface for customers to enter their payment details. It may involve user prompts, error handling, and visual feedback to guide customers through the payment process smoothly.
Communication with Payment Gateway
Once the payment information is validated, the front-end system communicates with a payment gateway, which serves as the intermediary between the merchant and the acquiring bank or payment processor. The payment gateway securely transmits the payment data for further processing.
Front-end processing is crucial for ensuring a positive customer experience, as it directly interacts with customers and handles their sensitive payment information. It plays a vital role in collecting, validating, and securely transmitting payment data to initiate the transaction process and facilitate the seamless flow of funds between customers and merchants.
What are Payment Gateways?
Payment gateways are technology platforms or services that facilitate the secure transmission of payment data between customers, merchants, and financial institutions. They act as intermediaries in the payment process, ensuring that transactions are securely and efficiently processed.
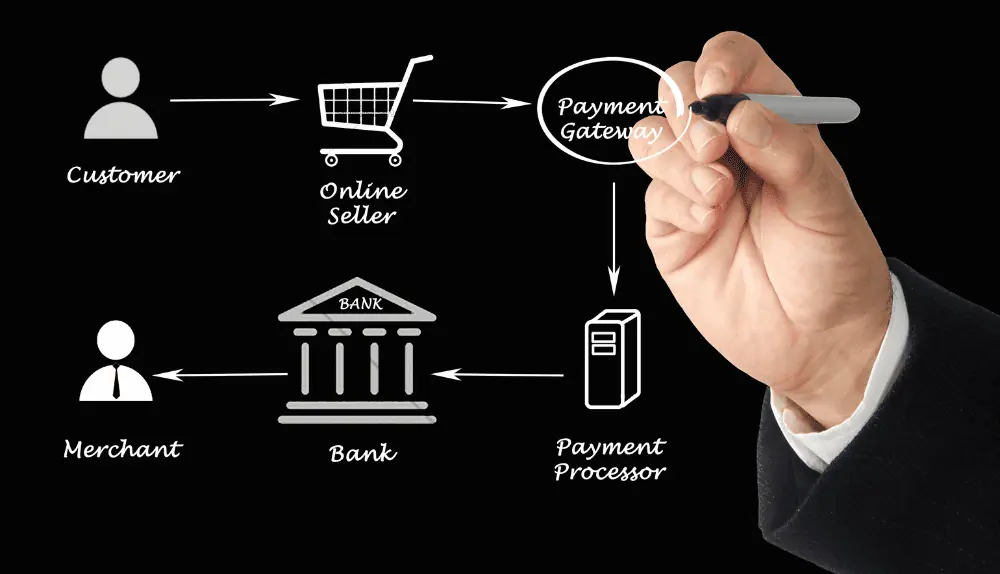
Here’s an overview of how payment gateways work:
Customer Initiates Payment
When a customer makes a purchase online or at a point-of-sale, they provide their payment details, such as credit card information or digital wallet credentials.
Encryption and Data Security
The payment gateway encrypts the customer’s payment data to protect it from unauthorized access during transmission. This encryption ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the information.
Authorization Request
The payment gateway securely sends the encrypted payment data to the acquiring bank or payment processor for authorization. This request includes information such as the transaction amount, payment method, and customer details.
Authorization and Response
The acquiring bank or payment processor evaluates the authorization request based on factors such as available funds, card validity, and potential fraud indicators. They respond to the payment gateway with an authorization code or decline message.
Communication with Merchant
The payment gateway relays the response from the acquiring bank or payment processor to the merchant, informing them of the transaction status. This enables the merchant to proceed with order fulfillment or notify the customer of a declined payment.
Settlement and Funds Transfer
If the transaction is authorized, the payment gateway facilitates the settlement process. It collaborates with the acquiring bank to transfer the funds from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account. This involves communication with payment networks and clearinghouses to ensure accurate and timely fund transfers.
Payment gateways support multiple payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets, and alternative payment options. They provide an essential layer of security by encrypting payment data, reducing the risk of sensitive information being compromised. Additionally, payment gateways often offer additional features such as fraud detection, recurring billing, and reporting tools to enhance the payment processing experience for merchants.
By integrating payment gateways into their systems, businesses can securely and efficiently accept payments from customers, expanding their reach and enabling seamless transactions in the digital world.
What is Back-End Payment Processing?
Back-end payment processing refers to the behind-the-scenes operations and systems that handle the authorization, settlement, and reconciliation of payment transactions. It involves the processing and management of transaction data after the front-end processing stage.
Here’s an overview of how back-end payment processing works:
Authorization Confirmation
Once the front-end payment processing collects and validates the customer’s payment information, it sends an authorization request to the acquiring bank or payment processor. The back-end processing handles this request and communicates with the issuing bank to verify the transaction’s validity.
Settlement
After the transaction is authorized, the back-end payment processing facilitates the settlement process. It collaborates with the acquiring bank and payment networks to transfer the funds from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account. This involves ensuring accurate accounting, reconciliation, and the secure movement of funds.
Fraud Detection and Risk Management
Back-end payment processing systems often employ sophisticated algorithms and tools to detect and mitigate fraudulent activities. They analyze transaction patterns, monitor suspicious behaviors, and apply risk management techniques to minimize the risk of fraudulent transactions.
Reporting and Analytics
The back-end processing generates reports and analytics to provide insights into transaction data. This includes information such as transaction volume, revenue, chargebacks, and other key performance indicators. These reports help businesses assess their financial performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
Integration and Security
Back-end payment processing systems integrate with various financial institutions, payment networks, and clearinghouses to ensure smooth communication and secure data exchange. They adhere to industry security standards and compliance regulations to safeguard sensitive payment data.
Reconciliation and Settlement Reporting
Back-end processing reconciles transaction records between the acquiring bank, payment processor, and merchant. It ensures that the settlement amounts match the authorized transactions and any discrepancies are identified and resolved. Settlement reports are generated to provide a detailed breakdown of the funds transferred, fees deducted, and other financial information.
Back-end payment processing plays a crucial role in managing the complex infrastructure that facilitates secure and efficient payment transactions. It handles the intricacies of authorization, settlement, fraud detection, and reporting, ensuring that funds are accurately transferred between parties and that businesses have the necessary insights to manage their financial operations effectively.
How Front-End and Back-End Payment Processing Work Together
Front-end and back-end payment processing work together in a coordinated manner to facilitate seamless and secure payment transactions. While they represent distinct stages of the payment process, their collaboration ensures a smooth and efficient payment experience. Here’s how front-end and back-end processing work together:
Front-End Collection and Validation
The front-end processing collects the customer’s payment information and performs initial validation checks. It ensures that the payment data is complete, accurate, and meets the required format. The validated payment data is then securely transmitted to the back-end processing for further processing.
Back-End Authorization
The back-end processing receives the payment data from the front-end and initiates the authorization process. It communicates with the acquiring bank or payment processor to verify the transaction’s validity, checking factors such as available funds, card validity, and potential fraud indicators. The back-end processing then sends the authorization response back to the front-end, indicating whether the transaction is approved or declined.
Front-End User Experience
The front-end processing communicates the authorization response received from the back-end to the customer. It provides a user-friendly interface, displaying transaction status and any relevant messages. For approved transactions, the front-end processing proceeds with order fulfillment or redirects the customer to a confirmation page. In the case of declined transactions, appropriate error messages or alternative payment options may be presented to the customer.
Back-End Settlement
If the transaction is authorized, the back-end processing manages the settlement process. It collaborates with the acquiring bank, payment networks, and clearinghouses to transfer funds from the customer’s account to the merchant’s account. The back-end processing ensures accurate accounting, reconciliation, and secure fund transfer.
Reporting and Analytics
Both front-end and back-end processing contribute to reporting and analytics. The front-end processing may collect data on customer behavior, conversion rates, or user experience metrics. The back-end processing generates reports on transaction volumes, revenue, chargebacks, and other financial indicators. These insights help businesses assess their performance, make informed decisions, and identify areas for improvement.
How Merchant Services Can Help?
Merchant services play a crucial role in supporting businesses by providing the necessary tools, infrastructure, and expertise to streamline payment processes and enhance customer experience. These services enable businesses to accept various forms of electronic payments, including credit cards, debit cards, and digital wallets, expanding their customer base and increasing sales opportunities.
By offering secure and efficient payment processing solutions, merchant services help businesses build trust and credibility with their customers, ensuring the protection of sensitive payment data and minimizing the risk of fraudulent transactions. Additionally, merchant services often provide reporting and analytics tools that offer valuable insights into customer behavior, transaction trends, and sales patterns, empowering businesses to make informed decisions and optimize their operations.
Furthermore, merchant services may offer additional services such as recurring billing, invoicing, and chargeback management, further streamlining financial processes and improving overall efficiency. With the support of merchant services, businesses can enhance their competitiveness, improve customer satisfaction, and drive growth in the dynamic landscape of electronic payments.
Final Words
In conclusion, payment processing is a complex and essential part of modern commerce, enabling businesses and consumers to engage in seamless and secure transactions. Front-end processing acts as the customer-facing interface, collecting and validating payment data, while back-end processing handles authorization, settlement, and reconciliation behind the scenes. These two components work in harmony, leveraging technology, security measures, and collaboration with financial institutions to ensure the smooth flow of funds and provide a positive payment experience.
Additionally, merchant services play a pivotal role by providing businesses with the necessary tools, infrastructure, and support to accept and process electronic payments. They enable businesses to expand their customer base, enhance security, streamline operations, gain valuable insights, and ultimately drive growth. As technology continues to advance and consumer expectations evolve, payment processing and merchant services will continue to adapt, fueling the ever-evolving landscape of digital commerce.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a chargeback?
A chargeback occurs when a customer disputes a transaction and requests a refund from their bank or credit card issuer. Chargebacks can happen due to various reasons, including fraud, product dissatisfaction, or billing errors.
How are online payments secured?
Online payments are secured through various measures, including data encryption, secure payment gateways, tokenization, and fraud detection systems. These security measures help protect sensitive payment information and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access or fraudulent activities.
Can I accept payments without a merchant account?
Yes, it is possible to accept payments without a traditional merchant account by using third-party payment processors or payment aggregators. These services enable businesses to accept payments without the need for a dedicated merchant account.
What fees are associated with payment processing?
Fees associated with payment processing can vary depending on the payment service provider and the specific services offered. Common fees include transaction fees (a percentage or flat rate per transaction), monthly fees, chargeback fees, and additional fees for value-added services.

