The Tor browser is frequently praised for its ability to enable anonymous web browsing. Its users range from human rights advocates seeking to evade authoritarian regimes to illicit online vendors operating in digital marketplaces. Tor offers a level of anonymity far beyond what typical internet browsing provides. However, it’s essential to recognize that Tor has limitations and can lead to a false sense of security if not used correctly.
This article will explore Tor’s key fundamentals: what it is, how it operates, and crucial tips for maintaining safety.
What is Tor?
The Onion Router (Tor) is an open-source network solely designed to help you keep your anonymity while browsing online. It does this by sending your web traffic through multiple encryption layers – similar to the layers of an onion, hiding what’s inside – hence the name “The Onion Router.” Your data travels through a series of nodes, including relays and servers, hiding your IP address and browsing from potential eavesdroppers. The Tor browser also lets you visit special “.onion” websites only accessible through Tor.
Image source
In the 2000s, the US government made Tor to protect sensitive internet communications. The US Navy wrote Tor’s original code, later releasing it to the public under a free and open-source license. Since 2006, The Tor Project nonprofit volunteers have kept Tor running for everyone online.
What is Tor Browser?
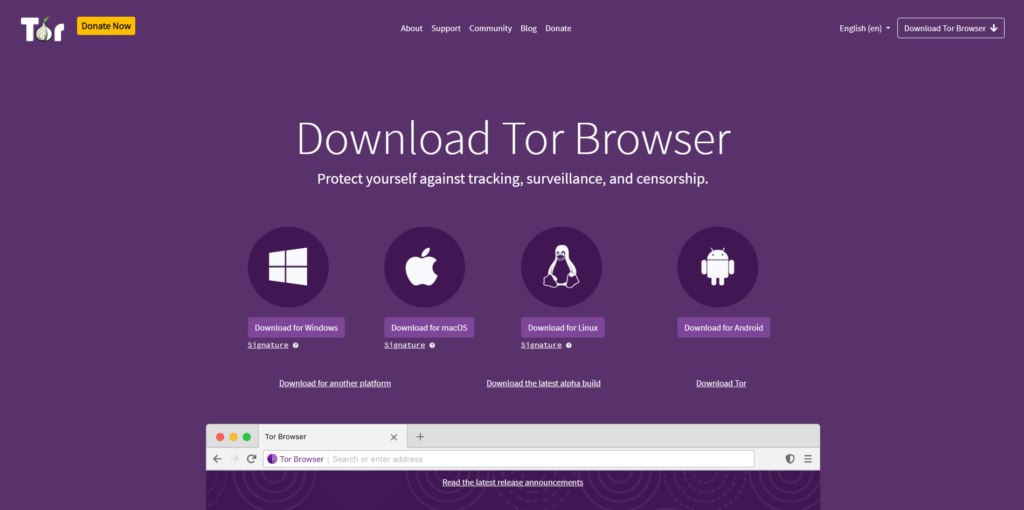
Image source
In straightforward terms, the Tor browser is software that provides users with a relatively high level of privacy when browsing the internet. The network and browser derive their name from how they route web activity through multiple routers, known as nodes, similar to peeling back layers of an onion. This process makes it challenging to trace and identify users.
However, there’s a strong association between Tor and the dark web because the Tor browser is frequently utilized for illicit purposes despite its original purpose not being intended for criminal activities. While the Tor browser is legal in many countries, some nations prohibit residents from accessing the network.
Are Tor and Tor Browser the Same Thing?
No, Tor and the Tor Browser differ in many aspects. Tor is a network enabling anonymous data transfers, whereas, the Tor Browser is an application letting users access this network when browsing online. Tor is a network built to secure online privacy by routing internet traffic through over seven thousand volunteer relays globally. This hides the user’s location and activities from those monitoring network traffic, whether its government, hackers, or ISPs.
Separately, the Tor Browser is a web browser that integrates Tor and other anonymity tools. This provides an easier, more direct method for private web browsing and simplifies accessing the Tor network securely.
How does the Tor Browser Work?
The Tor browser is a powerful tool that ensures user anonymity and privacy while browsing the internet. It works by utilizing a unique technique known as onion routing, which involves channeling the traffic through a series of international network nodes called onion routers. These onion routers are distributed across the world. They are designed to encrypt and redirect the traffic multiple times, making it difficult for anyone to trace the origin and destination of data packets.
This method of routing traffic through multiple layers of encryption provides a high level of security and privacy to the users, making it impossible for anyone to track their online activities or access their personal information. The Tor network operates by routing internet traffic through a series of nodes, each adding an extra layer of encryption to the data. These nodes are divided into three types: entry, middle, and exit.
- Entry nodes are responsible for establishing the initial layer of encryption and facilitating the connection to the Tor network. When a user requests a website, the entry node receives the request and encrypts it before forwarding it to the next node in the chain.
- Middle nodes are the next stops on the route. They receive the encrypted data from the entry node and add another layer of encryption to ensure complete anonymity. This makes it virtually impossible to trace the data back to its origin, a vital feature of the Tor network.
- Finally, the data arrives at an exit node. This node applies additional encryption to the data before it reaches the destination server. Once the data reaches the destination, it is decrypted by the exit node and forwarded to the server. This three-layered encryption process provides high privacy and security for Tor users.
What is the Purpose of the Tor Browser?

Tor Browser and a proxy server offer different levels of privacy and security. Tor Browser employs onion routing and multi-layer encryption to conceal your location and safeguard your data from various threats, such as hackers and web trackers.
It’s important to note that the primary function of the Tor browser is to enable anonymous web browsing and ensure online privacy. Its primary utility lies in evading surveillance and safeguarding personal information online. Here are some ways individuals or organizations use the Tor browser:
- Anonymity: The Tor Browser is a complimentary, open-source browser designed to anonymize your online activities and enable access to the dark web. It features tracker blocking and website isolation to prevent cross-site tracking, catering to users who wish to conceal their activities and location from governments, advertisers, or anyone tracking their internet use.
- Law Enforcement Use: Law enforcement agencies employ the Tor network for various purposes, including investigating suspicious services and websites on the dark web. Through Tor, officers can visit or survey websites without leaving government IP addresses in their web logs, enhancing operational security during sting operations.
- Accessing Restricted Content: Governments block access to specific websites or online content in certain nations. The Tor Browser assists users in circumventing these restrictions, allowing them to access blocked content and communicate with journalists and other contacts outside their country.
- Personal Information Security: The Tor Browser secures user data by encrypting traffic and masking the user’s IP address, safeguarding personal information from third-party collection. Individuals use it to protect their personal details and browsing preferences.
- Activists and Whistleblowers: Activists and whistleblowers use the Tor Browser to shield their identities from hostile forces or oppressive governments. It is a crucial tool for journalists and whistleblowers in researching sensitive subjects or disseminating confidential information while protecting their sources from potential harm.
- Illicit Use: Tor is also known to be utilized by various illicit organizations to hide their online activities, including but not limited to drug trafficking, cybercrime, and other forms of illegal commerce. This includes a wide range of illegal transactions and communications on the dark web, a segment of the internet that is intentionally hidden and accessible only through specialized tools like Tor.
Can Tor Browser Hide your IP Address?
Tor Browser effectively hides your IP address using its onion routing technology. This method ensures robust privacy protection by relaying your data through network nodes and employing multi-layered encryption.
As your data traverses through more than 7,000 independent network relays, it undergoes a process akin to the peeling layers of an onion. Each layer of encryption adds an extra level of security, making it exceedingly difficult for anyone to trace the origin of the internet traffic. When the data reaches its final destination, its true source is completely obscured.
This intricate process demonstrates the effectiveness of the Tor Browser in safeguarding data and concealing IP addresses from websites, internet service providers (ISPs), and governmental surveillance.
Setting Up the Tor Browser
Setting up and running Tor is no rocket science. It can be done in a few easy steps:
- Download Tor Browser:
Go to the official Tor Project website to download the compatible version with your device. Ensure you download from the official source to avoid fake or malicious versions.
- Installation:
After downloading, install Tor Browser on your device. The installation process varies slightly depending on your operating system but generally involves running the downloaded file and following the on-screen instructions.
- Running Tor Browser for the First Time:
You’ll encounter the “Connect to Tor” window upon launching the Tor Browser. This window offers you the choice to connect directly to the Tor network or to configure the Tor Browser for your connection if your access to the internet is restricted or censored.
If your connection is not censored, click “Connect” to start connecting to the Tor network. A status bar will display the progress of this connection. If you experience issues or the connection seems to stall, you might need to use the ‘Connection Assist’ feature or refer to the troubleshooting section for help.
In locations where Tor is blocked, Connection Assist can help by suggesting a bridge based on your location. If automatic suggestions don’t work or you prefer to configure your connection manually, you can select a bridge from a dropdown menu.
- First Connection and Configuration:
You may be prompted to configure your connection settings the first time you connect, especially if you’re in a region that censors Tor. Options include using a bridge or configuring network settings to bypass such censorship.
Tor Browser provides options to adjust these settings during the initial connection process for those using proxies or whose connection requires specific configurations.
- Using Tor Browser:
Once connected, you can use the Tor Browser much like any other web browser, with the added benefit of enhanced privacy and security. Remember, some websites may not be accessible via Tor due to their security policies against anonymous browsing.
To maximize your privacy and security while using Tor, keep the browser updated, consider using additional privacy tools and practices, and be mindful of the information you share online.
What Sets Tor Browser Apart from a Proxy Server?
A proxy server functions as a gateway between your device and websites or services on the Internet. When you use a proxy, your IP address and location are concealed from the websites you visit. However, it’s important to note that proxies do not encrypt your internet traffic, which means your data is still vulnerable to interception during transmission.
On the other hand, the Tor Browser provides a much higher level of security thanks to onion routing and multi-layer encryption. This combination of technologies obfuscates your location and safeguards your data from cybercriminals, web trackers, and other intrusive entities.
While it is possible to use a proxy server together with Tor Browser to conceal your use of Tor, it does not provide any additional cybersecurity benefits. Therefore, if you prioritize online privacy and security, Tor Browser is the way to go.
Is Tor Browser Legal?
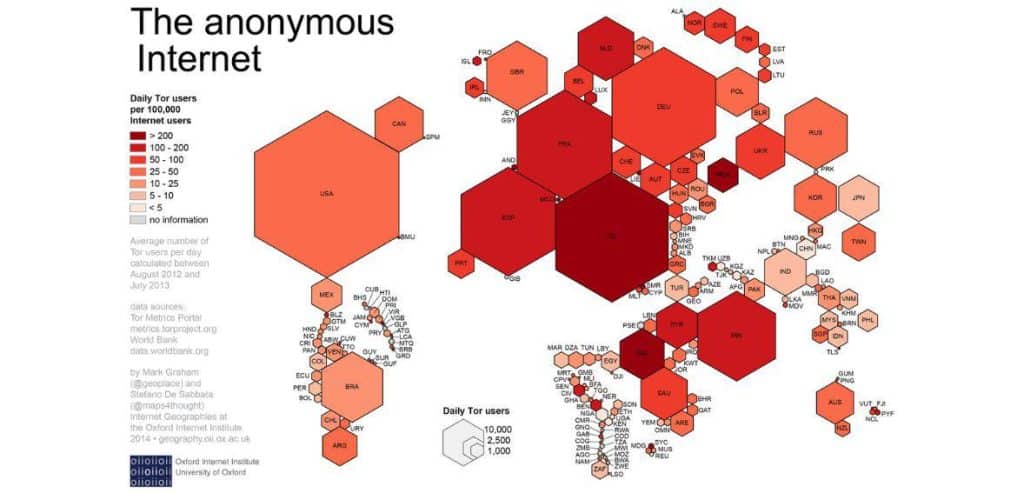
The Tor Browser is legal in the United States despite the misconceptions linked to its use due to associations with the dark web and criminal activities. The dark web, accessible via Tor, is not exclusively “wrong and harmful”; it houses numerous legitimate resources such as specialized Human rights organizations, secure communication services, and databases for research purposes. Utilizing the dark web for legitimate privacy protection is not unlawful if you avoid engaging in illegal activities.
However, employing Tor might inadvertently draw unwanted scrutiny to your online activities. Some Internet Service Providers (ISPs) might reduce your internet speed or query your use of Tor due to its association with privacy evasion. Additionally, certain governments monitor Tor usage closely, potentially tracking those who use it.
In specific countries, the use of Tor is directly prohibited. For instance, China has made anonymous browsing illegal, effectively banning Tor. Other nations, like Venezuela and Russia, actively discourage or block access to Tor. Verifying their legality within your jurisdiction is crucial before considering Tor or VPNs for anonymous browsing.
Tips to Consider Before Using Tor Browser
Navigating the Tor browser safely is a legitimate concern many users share. Given the potential online risks, taking precautionary measures to enhance your safety is essential. Here are several strategies to strengthen your security while using the Tor browser:
- Combine the Tor browser with a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to add an extra layer of security.
- Opt for the maximum security setting within the Tor browser to minimize the execution of browser code, which can reduce malware risks.
- Implement a firewall to safeguard your computer’s network integrity.
- Regularly update the Tor browser and any related applications or extensions to ensure you have the latest security enhancements.
- Incorporate a privacy-focused extension that secures connections by ensuring you access websites over HTTPS, automatically converting HTTP addresses to HTTPS where possible.
- Install reliable antivirus software to detect and neutralize threats.
- Refrain from signing into personal accounts, including social media and email, from avoiding data exposure.
- Use the Tor browser infrequently to avoid any detectable usage patterns.
- Install reliable antivirus software to detect and neutralize threats.
Conclusion
The Tor Browser offers robust privacy protection through onion routing and encryption. Despite its effectiveness, users must grasp its limitations and potential legal implications. Combining Tor with a VPN and adhering to security best practices enhances safety. Understanding the risks, including potential scrutiny from ISPs and governments, is crucial.
By adopting proactive measures like regular updates and cautious browsing habits, users can maximize the benefits of Tor while minimizing potential drawbacks. Overall, the Tor Browser empowers individuals to navigate the internet anonymously and securely, provided they approach it with awareness and caution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Tor Browser used for?
The Tor Browser protects your anonymity and privacy by using the Tor network. The Tor network has two main advantages: first, it stops local observers and your internet service provider from monitoring your online activity, including the websites you visit.
Is it OK to use the Tor Browser?
Generally, using Tor is considered safe, and Tor's Onion browser provides several advantages, such as enhanced safety and privacy. However, before using the Tor browser, users should be mindful of potential legal implications in their country and the possibility of being flagged for its usage.
What should I avoid on Tor?
Here are some tips to maximize your security while using Tor:
– Refrain from sharing personal data, as it compromises your anonymity.
– Activate the safest mode available.
– Visit only websites with HTTPS encryption.
– Exercise caution and avoid clicking on suspicious links.
– Keep your antivirus software updated.
– Consider using a virtual private network (VPN) for added protection.Do I need an antivirus for Tor?
While Tor can enhance security and reduce the risk of data leaks, it does not provide comprehensive protection against malware and online threats. Regardless of the browser you use, it's advisable to have antivirus software installed to safeguard against malware and other potential hazards.

