If you’re handling online payments, you’re likely familiar with the risks tied to card security and mode of transaction. Simply entering a credit card number for a purchase doesn’t guarantee that the person is the legitimate card owner. Running an online business exposes you to the potential of processing fraudulent transactions, which can have adverse effects, primarily manifesting as chargebacks.
When customers spot unauthorized transactions on their credit card statements, leading them to notify their bank and reclaim their funds, you not only miss out on the sale but also incur a chargeback fee. According to a recent study, fraud imposes a cost of 2.9% of the average merchant’s total revenue in 2022.
To safeguard your business, it’s crucial to verify transactions, ensuring that the cardholder is indeed the person claiming to be. This is where CVV or Card Verification Value and AVS or Address Verification System comes into play.
Understanding Card Verification Value
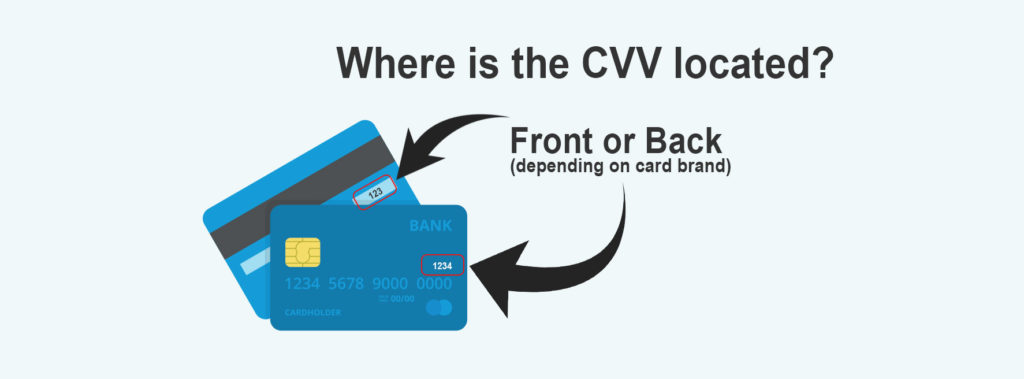
A Card Verification Value, or CVV allows enhanced security for both merchants and customers during transactions. There are two types of CVV codes, called CVV1 and 2, respectively. The CVV1 is embedded in the magnetic stripe of track 2 of a card. The purpose of the first CVV is to verify data stored on a card is valid and issued by a bank when used in person. The second and more prominent CVV2 is a three-digit code (Visa, MasterCard) printed on the back of credit and debit cards.
American Express cards have a ‘Unique card code’ that is four digits long and printed on the front. These codes are used in card-not-present transactions occurring over the Internet or Mail Order/ Telephone Order (MOTO) transactions as an added security feature to prevent fraudulent purchases. The code is meant to verify that the customer is the actual cardholder and that they have the card in their possession.
For Merchants
Merchants requiring CVV2 codes for their card not present transactions can dramatically reduce fraud in their businesses. Using this extra layer of protection can stop breached or fraudulent cards from going through. Avoiding potential retrievals and chargeback fees.

For Consumers
Entering your CVV2 code when purchasing online products verifies that you are who you say you are. Under Visa regulations, merchants cannot store CVV2 codes in their databases. This means any card numbers lost in a breach would be less useful. In this sense, a consumer is protected on both sides of a transaction, once when verifying the purchase and then again in terms of breach or fraud security.
CVV Codes And Their Meaning
| Meaning | Code |
| Match | M |
| No match | N |
| Not processed | P |
| Though not stated, it should be on the card. | S |
| The issuer is not certified | U |
| No response | X |
What Can You Do With These Codes?
While relying on CVV rules poses fewer risks of lost sales compared to stringent AVS restrictions—given that cardholders can easily refer to their cards— the recommended practice is to refrain from processing transactions that receive an N (No Match) response.
Whether or not it’s necessary to request the CVV depends on the fraud tolerance of each business. There are scenarios where it might be reasonable to waive the requirement:
- The product being sold has substantial profit margins.
- The business is experiencing rapid growth.
- The chargeback rate for the business is well below thresholds set by chargeback monitoring programs.
- The transaction is from a trusted user.
Some merchants enable customers to save and use payment methods for future transactions on their websites. While it may seem more convenient to skip the CVV confirmation step, merchants should consider implementing this security measure. Requiring customers to confirm their CVV for subsequent orders, especially when encountering an unrecognized device or changes to a shipping address, helps prevent fraudulent use by unauthorized individuals accessing the customer’s account.
Understanding Address Verification System
Address Verification System, or AVS, was designed by card issuers to assist in identifying any questionable transaction activity in credit cards and verifying that the cardholder’s address information matches what the banks have on file. The service is provided as part of a credit card authorization for mail-order/telephone-order transactions (MOTO) or Internet e-commerce transactions. A code is received with an authorization result that determines the address match’s accuracy level. This verification helps secure the most favorable interchange rates for the merchant.
Visa, MasterCard, Discover, and American Express support this service, and when paired with a CVV confirmation, the result is a secure, verified transaction. To verify a customer’s address, a merchant will need the cardholder’s billing ZIP code and the house or apartment number of the billing address. The merchant does not need to enter the cardholder’s street, city, or state. While AVS is not intended as absolute protection against suspicious transaction activity, it is an important step in securing non-face-to-face transactions. Host Merchant Services recommends that all merchants secure these types of orders with both AVS and CVV.
How Does It Work?
When your customer goes through the checkout process, they’re required to input a billing address. The card issuer then cross-referenced this address with the one they have on record. Following this verification, the card issuer transmits a response code to you, indicating the level of match between the addresses. The predetermined risk assessment in place with your payment gateway will dictate how you respond to these codes.
It’s crucial to understand that AVS only scrutinizes the numeric components of an address, such as the house number and postal code, excluding the alphabetical parts. Nevertheless, it remains a reliable tool for identifying potential fraudulent activities.
AVS Codes And Their Meaning
| Meaning | Code | Explanation |
| Full Match | Y/X | Postcode and address match |
| Partial Match | W/Z | The postcode didn’t match, but the Address matched |
| Partial Match | A | Neither address nor postcode matches |
| No Match | N | Information for the address is not available, or the issuer of the card doesn’t support AVS |
| Retry | R | Unavailable system, retry |
| Unavailable | U | Information for the address is not available, or the issuer of the card doesn’t support AVS. |
What Can You Do With These Codes?
While AVS responses provide merchants with options to counter fraud, being excessively restrictive can significantly and adversely impact sales. A straightforward application of AVS involves setting transaction restrictions based on the AVS response, potentially allowing only transactions where both the address and postal code match.

Accuracy in the billing address is directly relevant when sending something to a physical address. However, it’s essential to acknowledge that legitimate customers may occasionally input incorrect or incomplete information.
Moreover, inputting the accurate billing address holds direct relevance when acquiring physical goods. For instance, if a customer purchases concert tickets for digital delivery to their email inbox, the AVS code solely verifies whether the purchaser is familiar with the cardholder’s billing details. It does not, however, confirm the actual identity of the purchaser. Regrettably, when it concerns shipping addresses, fraudsters often exhibit a higher level of accuracy than the cardholders themselves. Furthermore, the AVS response may include data associated with the billing address.
How CVV & AVS Help Fight Fraud?
To combat fraud, merchants employ CVV and AVS in slightly different ways to verify ownership. When using an AVS credit card match, the merchant requests the customer’s address and ZIP code. Most POS systems can quickly confirm if the provided address matches the billing address linked to the card. On the other hand, CVV ensures that the customer has the physical card by requiring the code on the back of most credit cards (or on the front for Amex cards).
While it’s not mandatory to run CVV and AVS for keyed transactions, doing so is considered a best practice, even though it incurs a slightly higher cost (around $0.01 for a single transaction, with some providers potentially inflating these rates). Despite this minimal expense, the potential savings in preventing fraudulent transactions and subsequent chargebacks make it a prudent choice for safeguarding businesses.
The combination of AVS and CVV enhances the effectiveness of your security measures. While each on its own is reasonably effective, employing both significantly reduces the likelihood of falling victim to fraud and can be the decisive factor between a chargeback and a legitimate transaction. Strengthening security in your online business empowers you to identify and reject potentially suspicious transactions. Notably, 30% of chargebacks stem from purchases made with stolen credit cards. By incorporating both AVS and CVV into your online store, you can mitigate the risk of chargebacks associated with fraudulent transactions.
Conclusion
The integration of Card Verification Value (CVV) and Address Verification System (AVS) is vital for online businesses combating the rising tide of fraudulent transactions. CVV, requiring a three-digit code, enhances transaction security by validating the cardholder’s legitimacy, reducing the risk of chargebacks. AVS adds an extra layer by scrutinizing billing address accuracy, bolstering protection in non-face-to-face transactions.
The collaboration between CVV and AVS isn’t just a best practice; it’s a strategic necessity. Together, they form a robust defense, proactively identifying and thwarting suspicious activities. In a landscape where fraud incurs significant costs, these measures become integral to a comprehensive risk management strategy, safeguarding both revenue and reputation. Businesses navigating the complexities of online transactions must embrace the combined power of CVV and AVS to fortify the integrity of the e-commerce ecosystem and ensure secure digital transactions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does AVS mean on a card?
The Address Verification Service (AVS) serves as a fraud prevention system designed to curb fraud and charge-backs. AVS ensures that the billing address provided by the customer matches the one linked to the cardholder's credit card account.
Why does AVS reject transactions?
Address Verification Service (AVS) is a method employed by credit card companies to recognize and authenticate cardholder details. If the zip code or address supplied by the cardholder doesn't match the one on record, the transaction gets rejected.
What's the significance of CVV?
The primary purpose of a CVV is fraud prevention. It was created to enable banks to request an additional, easily verifiable set of numbers alongside the card number for authentication. While hackers may obtain card numbers through illicit means, obtaining the CVV numbers on cards proves more challenging for them.


